Introducing C data type
Every programming language deals with some data. For example to print any message it requires charterer or string type of data. To solve any mathematic expression it requires integral as well as real number (floating type) of data. C is very rich in data type. We can broadly divide all data type in c in three categories:
1. Primitive or fundamental
data type
2. Derived data type
3. User defined data type
List of data type in c
A complete picture of all c data types has been represented
by following figure.
Note: Apart from these basic data type there are few
other data types which have been defined inside header files which will be
discussed later.
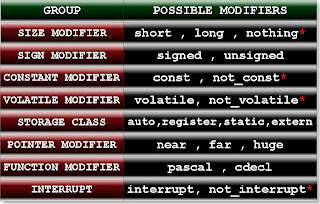
C data type modifiers
There are some keywords in c which modify the
meaning the meaning of above mentioned basic data type in c. On the basis of
properties of modifier we can categories the modifier in following eight
groups.
1. Size modifier
2. Signed modifier
3. Constant modifier
4. Volatile modifier
5. Storage class
6. Pointer modifier
7. Function modifier
8. Interrupt
In the above table modifier ending with * indicates
they are not keyword of c language. These modifiers are called as nothing
modifier since there is not any special keyword in which represents those
modifiers. If you will not write any thing it then compiler will understand you
are writing nothing modifier of those groups.
Meaning of
following word in the above table:
nothing: It is not short as well as not long.
not_const: It
is not constant. You can modify.
Not_volatile: It is not volatile.
not_interrupt: It is not sending interrupt signal.
Important
points:
1. Nothing modifier must be default modifier of that
group.
2. In LINUX GCC compiler there is not any concept of
pointer modifier.
Default modifier in c
1. Default modifier of storage class is auto when we
declared the variable inside any function and default modifier of storage class
is static when we declared variable outside of all functions. In other word we
can say if variable has declared locally then default storage class is auto and
if it has declared globally then default storage class of variable is extern.
2. Default storage class of function is extern.
3. Default modifier of pointer modifier depends upon
memory model. For detail knowledge click following link:
Modifiers in c
Explanation of modifiers in
c programming language by examples and questions
Rules for using modifier in c
Rule 1: We cannot use
two modifiers of same groups in any particular data type of c.
For example,
following declaration of c are illegal:
short long int i;
static auto char c;
signed unsigned int array[5];
pascal cdecl display();
Following are
valid declaration of c:
const volatile float f;
signed static long volatile int i;
Question: Is following declaration is valid in c?
1. intnear * far * huge *p;
2. char const * const *c;
3. short short int i;
4. const const int i;
Rule 2: We can write
modifier either before the data type or after the data type. For example, both
of following declaration is correct:
unsigned char c;
char unsigned c;
Rule 3: Order of
modifier including data type doesn’t affect the meaning of declaration. For
example all of the following have same meaning:
int const short extern i;
int extern const short i;
int short extern const i;
const int short extern i;
extern short const int i;
Rule 4: There is one
exception in rule 3. POINTER, FUNCTION and INTERRUPT modifier must be written
after the data type. For example, in the following declaration:
unsigned const char far *c;
char unsigned const *c;
char far unsigned const *c;
const char far unsigned *c;
far char const unsigned *c;
const unsigned far char *c;
Range of data types in c
Note: In the above table range of
float, double and long double has written only for positive numbers. But this
range is also true for negative numbers i.e. for range of float is -3.4*10^38
to -3.4*10^ (-38) and so on.
const modifier in c
Explanation of const modifier in c programming language
by examples, questions and answers:
In c all variables are by default not constant. Hence, you can modify the value of variable by program. You can convert any variable as a constant variable by using modifier const which is keyword of c language.
Properties of
constant variable:
1. You can
assign the value to the constant variables only at the time of declaration. For
example:
const int i=10;
float const f=0.0f;
unsigned const long double ld=3.14L;
2. Uninitialized
constant variable is not cause of any compilation error. But you cannot assign
any value after the declaration. For example:
const int i;
If you have
declared the uninitialized variable globally then default initial value will be
zero in case of integral data type and null in case of non-integral data type.
If you have declared the uninitialized const variable locally then default
initial value will be garbage.
3. Constant
variables executes faster than not constant variables.
4. You can
modify constant variable with the help of pointers. For example:
#include
int main(){
int i=10;
int *ptr=&i;
*ptr=(int *)20;
printf("%d",i);
return 0;
}